
Carlos Azevedo Biologia Celular Molecular Pdf File
Carlos Azevedo Biologia Celular Molecular Pdf Reader Average ratng: 3,9/5 5459reviews 40 Hadith For Islamic Schools Pdf Reader; - Yawman And Erbe History. - Carlos Azevedo Biologia Celular Molecular Pdf; 05/23.
Ex4 To Mq4 Decompiler Software Serials. Abstract 1,3-β- D-glucan is a fungal cell wall polymer synthesized by the multi-subunit enzyme 1,3-β- D-glucan synthase. A subunit of this integral membrane protein was first described as the product of the FKS1 gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae using echinocandin mutants. Other FKS1 genes were also reported for Candida albicans, Aspergillus nidulans and Cryptococcus neoformans. Here, we report the nucleotide sequence of the first homologous FKS gene cloned from the pathogenic fungus Paracoccidioides brasiliensis. An open reading frame of 5942 bp was identified in the complete sequence, interrupted by two putative introns, the first close to the 5′ end and the second close to the 3′ end of the gene. A promoter region is also described containing consensus sequences such as canonical TATA and CAAT boxes and, possibly, multiple sites for glucose regulation by creA protein.
Ess es1988s driver win7 64bit repair disk. Comment 8 Stephen E Clark Some files would play but repeat times and end, other files would play and repeat and not end – I would have to kill from another window. When the scan is complete, the driver update utility will display a results page showing which drivers are missing or out-of-date. If your driver is not listed and you know the model name or number of your ESS device, you can use it to search our driver archive for your ESS device model.
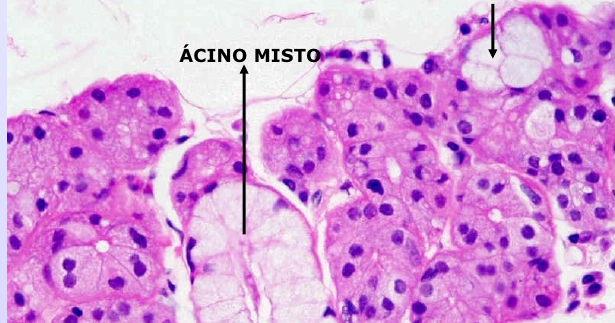
Get for free biologia celular e molecular carlos azevedo ebook in pdf. Download biologia celular e molecular carlos azevedo. File Size: 17.72 MB Format: pdf. File size: 18 MB: Date added: December 5, 2013: Price: Free: Operating system. Carlos Azevedo Biologia Celular E Molecular Pdf Do Pdf. Biologia Celular Carlos Manuel Gaspar dos Reis. 5, Biologia Celular e Molecular.
The deduced sequence of 1926 amino acid show more than 85% similarity to FksAp from A. Nidulans, and 71% to Fks1p and Fks2p from S. Computational analysis of P. Brasiliensis Fks1p suggests a similar structure to transmembrane proteins, such as FksAp, with the presence of two domains composed by hydrophobic helices that limit the putative highly hydrophilic catalytic domain within the cytoplasm.
The complete nucleotide sequence of PbFKS1 and its flanking regions have been submitted to GenBank under Accession No. Copyright © 2000 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. Post navigation.
Several homoplasmic pathologic mutations in mitochondrial DNA, such as those causing Leber hereditary optic neuropathy or non-syndromic hearing loss, show incomplete penetrance. Therefore, other elements must modify their pathogenicity. Discovery of these modifying factors is not an easy task because in multifactorial diseases conventional genetic approaches may not always be informative.
Here, we have taken an evolutionary approach to unmask putative modifying factors for a particular homoplasmic pathologic mutation causing aminoglycoside-induced and non-syndromic hearing loss, the m.1494C>T transition in the mitochondrial DNA. The mutation is located in the decoding site of the mitochondrial ribosomal RNA. We first looked at mammalian species that had fixed the human pathologic mutation. These mutations are called compensated pathogenic deviations because an organism carrying one must also have another that suppresses the deleterious effect of the first.
We found that species from the primate family Cercopithecidae (old world monkeys) harbor the m.1494T allele even if their auditory function is normal. In humans the m.1494T allele increases the susceptibility to aminoglycosides. However, in primary fibroblasts from a Cercopithecidae species, aminoglycosides do not impair cell growth, respiratory complex IV activity and quantity or the mitochondrial protein synthesis.
Interestingly, this species also carries a fixed mutation in the mitochondrial ribosomal protein S12. We show that the expression of this variant in a human m.1494T cell line reduces its susceptibility to aminoglycosides.
Because several mutations in this human protein have been described, they may possibly explain the absence of pathologic phenotype in some pedigree members with the most frequent pathologic mutations in mitochondrial ribosomal RNA. Introduction Human cells contain many mitochondria and each mitochondrion several mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) molecules. The absence of mtDNA genetic variation in a person is named homoplasmy.
However, homoplasmic mutations can be found in a particular individual when his/her mtDNA is different from a reference sequence, the revised Cambridge Reference Sequence (rCRS). If these mutations do not have phenotypic effect, they can survive in the populations for long periods of time. On the contrary, if mutations have very dramatic functional effects, they will be very quickly removed from the populations. Ebershpeher raspinovka razjyomov. In between, there are several pathologic mtDNA mutations with moderate phenotypic effects. These are the etiologic factors for some of the most frequent mtDNA diseases, such as the Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON) and the non-syndromic hearing loss (NSHL) (Fischel-Ghodsian,; Carelli et al., ). A common feature for these homoplasmic mutations with moderate functional effect is their tissue-specificity.